Mark Vakoc
Management Agent Install problem on AIX 5.3
If the process creates a core dump when executing the installation of the agent on your AIX 5.3 machine. Here is the important information from the core dump of the java process:
SIGSEGV received at 0x362220e4 in /opt/JDEdwards/Install/ismp001/libaixppk.so. Processing terminated.
If you see the above in the dump file then use this link to solve the problem. Follow the instructions closely and this should allow you to install the agent. It is a fix to the libaixppk.so for ISMP. Here is the link:
http://knowledge.macrovision.com/selfservice/microsites/search.do?cmd=displayKC&docType=kc&externalId=Q111262&sliceId=
iSeries EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server - Change Component processing by the Management Agent
Processing that occurs when you choose to register a pre-8.97 version of the Enterprise Server with Server Manager and then go to upgrade your server tools code to 8.97, Server Manager will automatically save the pre-8.97 version into a software component. That software component could subsequently be used to change from the current version back to the pre-8.97 version. So, Server Manager will allow you to roll back to that version that was registered when you first installed and setup your management domain. This is not specific functionality for the iSeries, but is good information to note as we understand what processing is going on in Server Manager. (NOTE: All work for any instance is done inside the agents jde_home\targets\"instancename" directory. Remember this note throughout the processing of the change component.)
Now, what happens during the processing to change out an iSeries EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server's tools code? First thing to note is that logging is fairly detailed as to the actual commands that are issued to the iSeries. Additionally, the return messages, even when successful, are logged to the agents log file. This is good for all troubleshooting. Second thing to note, as with any platform, the processing of changing out a tools release does a backup of the release being changed out as a first step into a temporary folder. This is for rollback purposes. If a step in the process of changing out the tools release fails a rollback will be executed. Now that you have these notes in the back of your mind, we can talk about the steps in the process.
First in processing is the backup itself. A save file is created for both the QSYS and IFS file system related to the EnterpriseOne code base, CRTSAVF commands. Next, if a printqueue directory exists in the IFS, a temp directory is created (MKDIR command) and the contents "moved" to the temp dir (MOV command). The reason for the quotes around the moved is based on the fact that the contents are not copied as this operation could take very long if the printqueue directory is large. The iSeries can "move" ifs objects much more efficiently than copy them. Next, a temp directory is created for the ini directory (MKDIR) and the ini file is "moved" to the temp directory just created (MOV command). Moved for consistency with the printqueue more than anything. Next, the actual save of the system library (i.e. - E812SYS) and the ifs directory (i.e. - E812SYS) is executed (SAVLIB command). Next each of the save files is copied into the IFS jde_home\targets\\ using the copy stream file command (CPYTOSTMF command). Now the backup of the existing system is complete.
Second in processing is replacing the old with the new. First we extract the software components contents into a temp directory. The contents that are important to Server Manager are scf-manifest.xml, system(SAVF) and krnlspec(SAVF). Next, the system library (E812SYS) is deleted (DLTLIB command). An important note here is that if any jobs have a lock on this library at this time, the DLTLIB will fail and the change will throw an Exception. So, make sure no locks are present before beginning this process. Next, a save file for the system library is created in a job QTEMP library (CRTSAVF command). Next, the extracted save file is copied into the newly created save file for the system library using copy from stream file (CPYFROMSTMF commands). Now we have the new qsys system save file that can be restored. Next, the system libarary is restored (RSTLIB command). A note here is that the library the system is restored into is the same name as the original library. Next, the creation of a subsystem (SBSD) is executed (CRTOWSBS command). Next, changing the data area BUILD_VER (DTAARA) in the system library is necessary (CHGDTAARA command). This matches the restored library name with the data area information. Next, delete the IFS E812sys directory (Java IFS file system utilities) . Next, a save file for the system folder is created in a job QTEMP library (CRTSAVF command). Next, the extracted save file is copied into the newly created save file for the system folder using copy from stream file (CPYFROMSTMF commands). Now we have the new ifs folder save file that can be restored. Next, the ifs folder (i.e. - E812SYS) folder is created. Next, the ifs folder changes owner to ONEWORLD (CHGOWN command). Next, the ifs folder is restored (RST command). Next, is the move of the printqueue and ini folders and contents. First make a directory for printqueue (MKDIR command). Move the contents into the new directory from the backup location (MOV command). Then change ownership to ONEWORLD (CHGOWN command). Second make a directory for ini (MKDIR command). Move the contents from the backup directory into the new directory, should just be jde.ini (MOV command). Then change ownership to ONEWORLD (CHGOWN command). Next, get the version value from the PTF.LOG file and set it for the instance. This is so we know the version of EnterpriseOne based on the value in this file.
So, if all the above steps complete successfully, we now have a new version of the EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server ready to run. Otherwise, at any point in the process that fails the backup system will be restored based on where in the process the failure occurs. Hence, there is as much level of commitment control going on as possible. Basically, the IFS and QSYS steps are tracked and then if all these are past then a full rollback should be attempted. I will not go through all possble scenarios with the rollback, but you will see the commands run to execute the rollback the same as the above steps.
Processing the iSeries EnterpriseOne Enterprise Server changeComponent is quite different than any other platforms Enterprise server, but the model is the same. Meaning that Server Manager will use common models for install, change and uninstall throughout the processing of all the EnterpriseOne server types.
SM Automatically Shutsdown on Signout
We have recently taken a few instances where the Server Manager process stops when you sign in and out of the Server Manager machine, or you connect remotely to the Server Manager machine and then disconnect from it. This issue has been SARd under 8688882.
SOLUTION:
This is actually a known Oracle issue with OC4J as documented in Metalink document 245609.1. For Server Manager, there are two methods to correct this issue. The first method is recommended since it does not involve editing the registry manually and it also ensures that the Server Manager install script gets modified so if it is rerun in the future, it will automatically add the service correctly. Method 2, however, is likely the quickest work around.
Method 1:
1) Make the following change in the installManagementConsoleService.bat which is located in your JDE_HOME\bin directory of the Server Manager machine:
from:"--StartParams=-Xmx512m;-Djde.home=%JDE_HOME%;-jar;oc4j.jar"
to:"--StartParams=-Xmx512m;-Xrs;-Djde.home=%JDE_HOME%;-jar;oc4j.jar"
Note the addition of -Xrs. This change REQUIRES that -Xrs come just after -Xmx512m.
2) Ensure that the Server Manager service is currently stopped.
3) Open a command prompt, and go to your JDE_HOME\bin directory.
Run:uninstallManagementConsoleService.bat
4) After the service uninstalls successfully,
Run:installManagementConsoleService.bat PASSWORD
where PASSWORD is your original jde_admin password from the server manager installation.
5) Start the service. It should now remain running after you log out.
Method 2:
1) Open the registry editor
2) Locate the following registry key:HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Apache Software Foundation\Procrun 2.0\SCFMngmtConsole1\Parameters\Start
where SCFMngmtConsole1 is the last part of the display name of the service
Set the "Params" value to:
-Xmx512m
-Xrs
-Djde.home=C:\jde_home
-jaroc4j.jar
(note the addition of -Xrs)
This change REQUIRES that -Xrs come just after -Xmx512m.
3) Start the service. It should now remain running after you log out.
Server Manager Logging - Part 3
- registering/installing E1 managed instances
- registering and managing IBM WebSphere and Oracle Application Server
- managing the configuration file(s) for E1 managed instances
- starting/stopping E1 servers and the J2EE servers
- performing tools release upgrades/downgrades for E1 servers
- discovering and sending log files to the management console for viewing
Before we dig too far into the log files themselves let's get an understanding of the logging system used. Server Manager makes use of the standard java logging framework. This framework is different than the logging engine used by most other E1 software components which are based on the jdelog.properties configuration file.
The java logging framework exposes, and we make use of, seven levels of logging as outlined below in descending order
The default level for agent logging is FINE, which is appropriate for most occasions. It may be desirable to change the level to FINER or FINEST to troubleshoot an issue, or move it to a higher level, such as INFO, for some reason. If the agent is running and connected to a management console you may change the level directly from the console. Located on the left hand side of the page for the management agent is a section entitled 'Managed Home Details'. In there is a dropdown for 'Agent Log Level'. The current value will be shown.
I do not recommend permanently keeping the log level at OFF, SEVERE, WARNING, CONFIG, or INFO. You never know when you may need the additional information provided by the FINE level. The agent will automatically remove old log files so there should be no concern of log files filling a disk.
Embedded Agent LoggingThe E1 enterprise server and E1 HTML server all contain variants of the management agent. In the embedded form the logging messages generated by the management agent are not typically logged. It may be desired to enable the same logging for the embedded management agents. To do so simply add the following line to the <agent_install>/config/agent.properties file.
After adding this line and restarting the E1 managed instance series of log files will appear in the <agent_install>/logs directory. The filename of the log files will be the instance name of the E1 server.
Stack Traces: some log messages may contain stack traces. This information is useful for identifying the source of the message. A stack trace is not always indicative of a problem. The level of the message is much more indicative. Stack traces for INFO, FINE, FINER, or FINEST messages are included to provide more information and is not an error.
Server Manager Logging - Part 2
During the running of the installation program the log file created, named smha_is_install.log, is located in platform specific temporary directory. The
InstallShield installer creates a temporary directory named something like 'ismp01' underneath the system temporary directory. On UNIX based platforms and the iSeries this temporary location is usually /tmp and on Windows the temporary directory is identified by the %TMP% environment variable, usually Documents and SettingsusernameLocal Settingstemp.
After the installation is complete the smha_is_install.log is copied to the installation location supplied during the installation wizard.
Compared to the installer for the management console discussed in part one of this series the management agent installer is very trivial. The installer is responsible for performing the following:
- Creating the managed home directory structure
- Installing the Java based managed home agent and any configuration it needs
- Creating the Windows service used to start and stop the agent [Windows only]
- Creating the startup and shutdown scripts
- Installing the Java JDK used by the managed home agent
- Installing the Oracle Configuration Manager agent [non-iSeries platforms]
Server Manager Logging - Part 1
So where do you go when something in SM isn't working just right? We spent considerable time attempting to log often and use meaningful messages within SM. That said it is a distributed architecture with components contained on the console machine, agents installed on remote machines, and more agents built into the E1 products themselves. This post will help you identify which logs you should be looking at, where they are, how to configure them, and what to look for. For the sake of being able to finish the article eventually I'll just focus on the SM logs.
Installation Logs - Management Console
We begin with looking at the log files generated during the installation of the management console. These can be helpful if there are problems installing the management console application. Once the console is successfully installed and you are able to sign-in to the web application these logs are no longer relevant for any purpose and may be removed, if desired.
The management console is installed using an InstallShield based installer. This installer is responsible for creating the <console_install> directory, extracting all the component files that make up SM, configuring the integrated J2EE server, and deploying the management console web application.
The primary log created by the installer is located in <console_install>logssmmc_install.log. This is the first place you should look if you are having problems installing the management console. This log will probably go down as the most cryptic of the log files to analyze but somewhere in there is good information. One thing to note is if something goes wrong during the installation the installer will roll back the changes already made. This may result in error messages and other possibly confusing messages in the log file. In the case of a failed installation you want to find the first thing that went wrong in the log file before it started rolling back the installation.
The bulk of the messages in the smmc_install.log file will detail the extraction of files from the installer application to the <console_install> location. Near the end the installer performs the configuration of the J2EE container and deploys the management console application. The first task is to configure the administrative user for the J2EE container using the credentials provided during the installer wizard. The smmc_install.log will contain the following lines:
(Jul 31, 2007 12:40:14 PM), Install, com.installshield.wizard.platform.win32.Win32ProductServiceImpl, msg1, installing Exec Action (execJaznJar)
(Jul 31, 2007 12:40:16 PM), Install, com.installshield.wizard.platform.win32.Win32ProductServiceImpl, dbg.install, JVM memory after installing Exec Action (execJaznJar): free=9833152 total=23748608
At the same time two new log files will appear in <console_install>logs: jazn_stdout.log and jazn_stderr.log. These are the stdout and stderr output from running commands contained in the jazn.jar java application delivered with the J2EE container. The stderr file should be empty. Any content in the file is indicative of an error and will cause the installation to fail. If the jazn_stderr.log file is not empty you should investigate the cause of any errors detailed within.
The next step performed is to install the Windows service used to start and stop the management console. This is performed by running the delivered script <console_install>bininstallManagementConsoleService.bat. The following lines in the smmc_install.log file indicate when this batch file is called:
The installManagementConsoleService.bat creates a log file named <console_install>logsinstallManagementConsole.log. The contents will look something like:
Now that the J2EE server has been configured with the administrative password and the Windows service created its time to start the container. The batch file <console_install>binstartManagementConsole.bat is invoked and you will see lines along the lines of:
The output of the startManagementConsole.bat is written to the log file <console_install>logsMCDeploy_stdout.log. The first two lines of the file will contain something like:
It may take a while for the J2EE container to fully start up. To ensure the container is actually running before the management console application is deployed the installer will repeatedly run a command line program that will check if the server is actually running. You will see this in the log file:
The installer will be looking for a success message emitted by the program run. If not found it will wait a bit and re-run the command, eventually giving up. The responses are appended to the MCDeploy_stdout.log. The success message looks like
Once the J2EE container is validated as running the management console application is deployed to it. The deployment is performed through a command line program, the running of which is shown below:
The output of the deployment operations are also appended to MCDeploy_stdout.log and should look something like:
Any errors or problems that occur during the startup, running validation, and deployment will appear in the log file <console_install>logsMCDeploy_stderr.log. The installer will check if there are any errors contained within this file and if so terminate and rollback the installation, as shown below:
(Jul 31, 2007 12:42:00 PM), Install, com.installshield.wizard.platform.win32.Win32ProductServiceImpl, msg1, installing Log File Error Check (logFileErrCheck)
(Jul 31, 2007 12:42:00 PM), Install, com.oracle.e1.install.common.ISMP.product.LogFileErrorCheck, msg1, Beginning stderr log checks.
(Jul 31, 2007 12:42:00 PM), Install, com.oracle.e1.install.common.ISMP.product.LogFileErrorCheck, msg1, Checking for errors in: D:servermanagerdemosystemlogsMCDeploy_stderr.log
(Jul 31, 2007 12:42:00 PM), Install, com.oracle.e1.install.common.ISMP.product.LogFileErrorCheck, msg1, No errors in the stderr logs, continuing the installation.
In case you forgot the information you entered, such as the HTTP port to use for the management console, a readme.txt file is created in the <console_install> directory. After creating the readme.txt file the installation is essentially complete.
Next Time
Now that we have the management console installed it's time to start installing some management agents, and looking at their log files.
Some Kind Words on 8.97
Oracle Delivers Cool Tools for JD Edwards EnterpriseOne
Monitors in Server Manager
Monitors
Most of my posts thus far have been about installation, troubleshooting, and other server manager basics. Today begins a series of posts outlining the new or enhanced capabilities provided by SM.
Monitors are the mechanism by which administrators can be alerted through e-mail when an event of interest occurs. Much of this functionality is a direct carryover from that provided by the SAW SMC infrastructure in previous tools releases with some significant enhancements to boot.
As you may be aware by now Server Manager is a complete replacement for SAW and SMC. Among the other benefits, such as deployment and configuration management, we wanted to enhance and make easier to use the functionality provided by the SAW application.
While evaluating the SMC monitoring capabilities we identified the need to improve it in the following ways:
* Simplify the setup required to monitor servers and configure events of interest
* Enhance the monitored events to include some key items of interest, such as a user being unable to login to the E1 HTML Server
* Permit configuration of the hours in which alert e-mails should be sent for sites that make use of multiple administrators that are responsible for particular times of the week
* Maintain a history of past events and record the e-mail messages that were sent
We also changed the mechanism by which the events of interest are obtained. Beginning with 8.97 our server products contain an embedded variant of the management agent that provides server manager with the runtime information about the servers. Using this mechanism to obtain events provided two primary benefits: many of the events are reported to SM immediately upon occuring and events can be obtained from clustered or multi-JVM configurations for our web based products.
Currently monitoring is supported for our enterprise server and HTML server products only.
To get started select the monitors link from the quicklinks section. Note you must be signed into the management console as the jde_admin user or another user that as been granted the 'monitorConfig' permission to make changes to the monitoring configuration.
SMTP Configuration
The first step is to configure the SMTP mail server that will be used by server manager to send emails. Simply supply the mail server name, TCP/IP port to use, and sender email to use as the 'from' address. Some SMTP servers may require the sender email be from the same domain the mail server is configured to use. Note: SMTP servers that require authentication to send emails is not currently supported.
After making any changes you may supply an email address to test the settings. Server Manager will send an email to the supplied address to ensure the mail server configuration is correct.
Getting Started
The next step is to create a new monitor. You may have as many monitors as you wish. For example you may wish to create multiple monitors that listen for different events and each have different email recipients. Enter a name for the new monitor and select the 'Create' button. You will be redirected to a page used to configure the newly created monitor.
The first option in the general settings controls how often the monitor should poll for events. Some events will be detected immediately; when they occur a notification is sent to the management console and then to each running monitor. If this event is enabled for a particular monitor an email will be sent immediately. Other events are polled on a periodic basis. For example checking the free disk space on an enterprise server occurs on this period poll. You can change the frequency in which the monitor will check for these events.
Checking for monitored events is a low impact activity. That said if you have a large number of monitors it may be advisable to increase this interval from the default of 30 seconds.
Secondly you may configure whether this monitor should be automatically started when the management console application is started. Regardless of this selection an authorized user may start and stop monitors at any time using the previous page.
Instance Selection
The next step involves selecting the managed instances that this monitor should observe. Simply move the desired instances from the available options list to the selected options. Note that any changes made here on a running monitor will take effect immediately; the monitor need not be restarted.
Event Selection
Now that we have selected which managed instances we should monitor we now need to select which events we wish to observe. You do so by simply selecting the events of interest in the next section of the page. Each event has a help box next to it describing what the event is and when it may occur.
Some events may have threshold values that allow you to define a limit that, once reached, will trigger an email notification. The example below shows the limits for simultaneous users.
Once a threshold limit is reached on an enabled event a email notification will be sent. Notifications will not be resent unless the threshold goes higher. Consider the simultaneous users event. If we set the threshold to 50 we would receive a notification once 50 users are on at the same time. If two users sign off and two new users sign back on we are back at 50 simultaneous users. An email will not be sent; an email for 50 users has already been sent. If another user signs on, so we are at 51 sessions, and email will be sent; we have gone higher then the highest threshold reached.
I won't go into what all the events are in this post; they are documented with online help within the application.
Notification Hours
For a particular monitor you may specify which hours in the day and which days of the week email notifications should be sent. This may be helpful for those who administer in shifts. Those interested in events on weekdays may be different then those interested in weekend events, for example.
When you create a new monitor the default will be to enable notifications for all hours of all days. You can change this by modifying the times for each day using 24 hour notation. To disable events for an entire day simply set the start time and end time to both be 00:00.
The management console will use the clock and time zone information provided by the JVM on which it runs. That is the times should be considered to be the times as known to the management console machine.
Email Recipients
Finally we specify the email recipients that should receive notifications. You may add as many recipients as you wish. Any changes made to this list will take effect immediately; you need not restart the monitor.
Emails are sent individually to each recipient defined for a monitor using the from address configured previously. The subject and content of the email will contain details of the event. The mail format is plain text and is suitable for email, pager, and SMS mailboxes.
If an email could not be sent for any reason the failure will be recorded in the monitor's history, as discussed below.
Monitor History
Server Manager maintains a history for each monitor. Each start of a monitor will be listed in the monitor history.
You may view the history of a particular monitor to see all the events that occurred and the emails sent by clicking the appropriate icon in the grid row.
Each event that occurred will be listed along with the same type if information that was contained in the email sent. A grid will contain a listing for each email recipient of the monitor showing the successful sending of the email, an email that wasn't sent because it was outside the notification hours configured, or a email that failed to send for some reason such as an invalid recipient.
You may delete the monitor history if you no longer wish to view it. You may not delete the history for an actively running monitor.
Cloning Monitors
We have made it easy to clone an existing monitor. Simply select the corresponding icon in the 'Create Duplicate' column in the list of available monitors.
All the settings, selected managed instances, events, notification hours, and email recipients from the selected monitor will be copied to a new monitor definition. This makes setting up monitors for shifts much easier; the events and other setup need not be configured multiple times.
Summary
Hopefully you see that setting up and using monitors in Server Manager is much easier than previous solutions and the added events make administering your E1 servers much easier. Dig in, play with monitors, and enjoy.
UPDATE: I think the issue with missing images has been resolved.
Using NFS partitions on AIX
So what does this have to do with E1 and Server Manager? The second step of performing a tools release change involves deleting the existing tools release. The caching of the shared libraries, and thus the presence of the .nfs#### files in the $EVRHOME/system/lib directories will prevent the removal of the system directory. This will cause the tools release change to fail, and the previous tools release will be restored. Even root cannot delete this .nfs files directly.
Agent Update Packs
You may notice an entry named 'Agent Install Pack 7' of type 'Management Agent Installer Bundle'.
What is this? Well, in a previous post I mentioned that we have two separate downloads for Server Manager for each tools release.
- A large (~1 GB) Installer, and
- A much smaller (< 50 MB) console update
There's actually a third possible download from the update center: a new agent update pack. This contains items that are rarely going to change with each tools release update. Specifically it contains the platform specific managed home installer for all the platforms we support and the platform specific Oracle Configuration Manager agent that is installed along with the managed home.
These items are rarely updated because
- The managed home agent installer obtains the actual agent codebase from the management console, thus installing whatever is current with the console application
- The Oracle Configuration Manager agent will automatically update with the latest version provided by Oracle, therefore not requiring OCM updates with Server Manager
How do I know if I need a new agent installer pack? Should we need to update the agent installer pack we will create and add the package to the Update Center. Navigating to the 'Management Agents' page will tell you if a new agent installer pack is required. For example, assume:
- We updated the agent install pack with a particular tools release of Server Manager
- You have applied that SM update to an existing SM installation
- You want to install a new managed home agent
What if I delete the existing agent installer pack? This software component is treated just like any other software component; that is you can delete it either through SM or directly from the file system. If you have deleted the agent installer pack and navigate to the 'Management Agents' screen you will be instructed to obtain the installer pack from the Update Center.
Since we have not had the need to rev the installer pack it is not currently available for download from the Update Center. So, in the case you accidentally deleted the existing installer package you may obtain it only by performing a new SM installation and copying/uploading the file from the new install to the existing installation. After doing so you may uninstall the new SM console just installed.
The file will be named something along the lines of agentPackage7.jar and will be located in the directory INSTALL_BASE/components, where INSTALL_BASE refers to the installation path of the SM application.
Starting UNIX Enterprise Servers
8.11SP1 introduced the platform pack, an improved installation program, used to install the enterprise server and database files. The platform pack did away with the .oneworld script instead favoring a more robust script named enterpriseone.sh located in the $EVRHOME/SharedScripts directory
The user's .profile was modified to call the enterpriseone.sh script during login.
8.97.0.0 Server Manager
The 8.97.0.0 release of Server Manager contained several issues around properly setting up the environment prior to invoking the start/stop scripts. Most of these issues have been addressed by 8.97.0.1 and as such all UNIX based installations should immediately upgrade server manager to 8.97.0.1.
8.97.0.1 Server Manager
Server Manager starts/stops the enterprise server by calling the script startEntServer.sh/stopEntServer.sh located in the $EVRHOME/SharedScripts location. The scripts are dynamically created each time the server is started or stopped. If that directory does not exist (as it may not in 8.9, 8.10, or 8.11) it will be created. The startEntServer.sh and stopEntServer.sh scripts will do the following tasks
- Include the .oneworld or .enterpriseone.sh script, depending on release
- Call the RunOneWorld.sh or EndOneWorld.sh script
There remains one pending issue for IBM UDB users: prior to 8.11SP1 the installation instructions required the user to add a call to the db2profile script used to setup the environment needed for the UDB binaries and environment variables. The documentation instructed the user to add this call to the operating system user's .profile. The startEntServer.sh/stopEntServer.sh scripts did not directly include the db2profile script call, resulting in an enterprise server started using server manager failing to connect to UDB. The jde.log files for the kernel processes that establish a database connection would include numerous errors indicating that libodbc.[sl or so, depending on platform] failed to load.
8.97.0.next Server Manager
The next tools release will include some fixes to address the UDB issue mentioned above. As the startEntServer.sh and stopEntServer.sh files are created, during start or shutdown, the management agent will parse the user's .profile looking for a call to the db2profile script. If found it will add a call to this script thus properly setting up the UDB environment.
If you are using 8.97.0.1 Server Manager in a UDB environment you can easily workaround this issue by adding a call to the db2profile into the .oneworld script rather than the .profile.
Depending on how the user is setup, how the db2profile script is called, and the virtually unlimited permutations we realize that our .profile parsing logic may not always find the db2profile script. There may also be other environment setup that we did not anticipate. Since the startEntServer.sh and stopEntServer.sh scripts are dynamically created it is not possible to modify these files directly. To address this a check for the scripts startExtras.sh or stopExtras.sh has been added to the dynamically created scripts. We do not deliver these scripts, however, if present they will be invoked. This permits the administrator to add any additional setup each time the server is started or stopped. These scripts are located in $EVRHOME/SharedScripts and are available for all apps releases.
The JVM Issue
The 8.96 tools release introduced Java based kernel processes using a bundled JVM for the metadata kernel. 8.97 makes further use of this capability for both the BI Publisher and Server Manager kernel processes. The required JVM is bundled with the tools release (except iSeries where it is built-in to the OS).
The server manager managed home agent also includes a bundled JVM (again, except for iSeries). The 8.12 platform pack (and the included enterpriseone.sh) shell script properly configures the LD_LIBRARY_PATH or SHLIB_PATH (depending on platform) to properly define the directories in which shared libraries should be loaded.
The scripts created by the installers/platform packs prior to 8.12 did not have these additional environment configuration parameters needed to properly startup the enterprise server. With Server Manager the startup scripts are invoked by a Java process (our bundled JVM, based on 1.5). The JVM will modify the LD_LIBRARY_PATH or SHLIB_PATH to include locations specific to the 1.5 based JDK we deliver. This will conflict with the 1.4 JDKs delivered with the enterprise server tools release.
If you installed your enterprise server using the 8.12 or later platform pack stop reading; this issue will not affect you. If you initially registered your enterprise server using the 8.97.0.2 release or later stop reading; we have fixed the issue.
If you installed your enterprise server using 8.11SP1 or earlier AND registered your enterprise server using 8.97.0.1 or earlier server manager you may still have an issue. We modified, during the registration process, the .oneworld or enterpriseone.sh script to properly setup the LD_LIBRARY_PATH/SHLIB_PATH for you. However, there was a flaw that you may have to manually correct. If you look in these files you will see a line that was added by server manager that defines the JVM_LIB environment variable, and the LD_LIBRARY_PATH/SHLIB_PATH are modified to include it. The flaw, however, is in the order added. We appended the JVM_LIB environment variable to the existing LD_LIBRARY_PATH/SHLIB_PATH. Instead it should have been prepended to it.
To resolve this issue edit the appropriate file and ensure that LD_LIBRARY_PATH is redefined to be something like:
Summary
If you registered your enterprise server using 8.97.0.2 or later server manager don't worry -- all these issues have been resolved.
If you registered your enterprise server using 8.97.0.1 or earlier server manager and your enterprise server was installed using 8.11SP1 or earlier platform pack/installer you may need to modify the LD_LIBRARY_PATH/SHLIB_PATH to move the JVM_LIB definition.
If you use UDB and you are using 8.97.0.1 or earlier server manager and your enterprise server was installed using the 8.11 or earlier installer you may need to add a call to db2profile to the .oneworld shell script.
Installing Server Manager for Non-English Machines
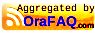
The Management Kernel
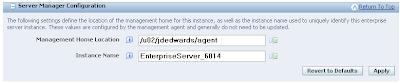
The SAW Kernel
The Although SAW has been replaced with 8.97 there are still portions of the SAW infrastructure that are used by server manager. On the enterprise server the SAW kernel is still used. The Management Kernel (Java) exposes the runtime information using the JMX standard. It obtains much of this information by sending JDENET messages to the SAW kernel.
It is advisable to continue to run multiple SAW processes. The information exposed by the management kernel is collected periodically, approximately every 30 seconds. After that elapsed time JDENET messages are sent to the SAW kernels to collect the information. Having multiple SAW kernels will ensure that the information update to the management kernel occurs quickly and reduces the likelihood of any of these messages timing out.
Troubleshooting
In reality there is very little that needs to be known about this kernel. That said if the runtime information isn't available for a running enterprise server it may be desirable to investigate the log files for the kernel. There are two sets of log files of interest: the jde/jdedebug.log and the java log files.
The first place to check is the server manager jde.log. Since the process list isn't available (that's what we're troubleshooting) we'll have to randomly go through the log files exposed on the management page for the enterprise server until we find the management kernel. A successful startup is shown below. If there are any errors about starting up the JVM, loading the SM classes, or any other content in this log file this is the first place to look.
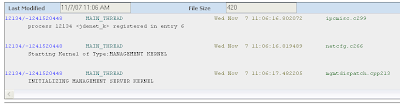 If there are no problems indicated in the JDE.LOG you may look at the java based logs. Since this is standard E1 Java code, logging is configured in the jdelog.properties file contained within the system/classes directory. For each log defined in the jdelog.properties you will see a corresponding log file created for each java based kernel process. Since multiple processes can be defined for the other java kernel types (metadata and xml publisher) the process id is added to the filename, as shown below:
If there are no problems indicated in the JDE.LOG you may look at the java based logs. Since this is standard E1 Java code, logging is configured in the jdelog.properties file contained within the system/classes directory. For each log defined in the jdelog.properties you will see a corresponding log file created for each java based kernel process. Since multiple processes can be defined for the other java kernel types (metadata and xml publisher) the process id is added to the filename, as shown below: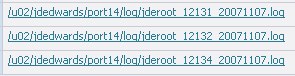
Summary
The management kernel provides server manager powerful new monitoring capabilities. The operation of the management kernel can generally be ignored and should only be of concern should runtime information not be available for a particular enterprise server in the management console web application.
Improving Database Connection Pools
The maximum size, initial size, growth increment, and other parameters are configured in the JDBJ Database Configuration -> JDBj Connection Pools configuration parameters. Refer to the Server Manager Guide for information about the particular settings.
For each effective database connection, or connection URL, a pool of connections is created upon first request. What is a connection URL? The actual logic varies based on database type but can be summarized as a combination of the connection information (server, port, SID, etc) appended by the name of the proxy database user. A good way to think of it is evaluating the actual connection details defined by an EnterpriseOne datasource. For example a typical Oracle database based installation will use the same SID for each datasource. Thus regardless of whether the datasource is 'System - 812' or 'Central Objects - PD812' it all boils down to the same database -- the SID. In this case the connection URL will be the concatenation of the SID with the name of the proxy user.
Other databases may use more complex naming conventions for the connection URL. For example SQL Server based datasources will look something like 'jdbc:sqlserver://DENDSQWN01:1433_JDE_DEVELOPMENT_true_JDE'. This URL includes the server name, listening port, physical database name, unicode enabled, and proxy user.
The active database connections may be viewed using Server Manager. Navigate to the HTML server of intesrest and select 'JDBj Connection Caches' from the runtime metrics. You will see all the connection pools that have been established.
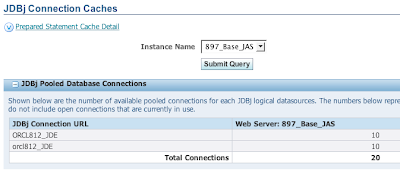
In the screen shot above you can see I actually have two sets of 10 database connections to two different connection URLs. The thing is these are the same database differing only by case. This didn't seem like a good thing so I went through my database datasources (F98611) and found I used all upper case there. I then went through the configuration metrics in server manager for my JAS server and found both upper and lower case uses of the Oracle SID. Changing those all to uppercase and restarting my server resulted in a single pool to the database.
Multiple JVMs in OAS
A multi-JVM configuration allows a single URL to be load balanced onto two or more JVM processes for a single OC4J container. The Apache http server will automatically load balance users onto a particular JVM where their session will remain for the duration of their sign-in. A multi-JVM setup is not a failover clustering configuration; that is, if a JVM were to crash all the user sessions on that JVM will also terminate.
The number of simultaneous JVMs is configured at the OC4J container level. To view or modify the JVM count navigate to the management page for the Oracle Application Server within Server Manager. In the middle of the page you will see a section listing each J2EE container (OC4J instance) within the OAS instance.
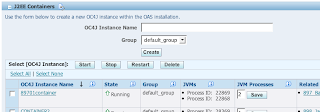
Listed next to each OC4J instance is the JVM Processes edit and a list of active JVMs if the container is currently running. To modify the JVM processes edit and save the change. Changes will take effect the next time the container is started. Starting or stopping a JAS instance within server manager starts/stops the corresponding container.
Runtime Metrics
Server Manager will automatically detect the multi-JVM configuration and display all the runtime metrics (user sessions, database caches, et. al) separately for each JVM. Each JVM is assigned, by OAS, a unique JVM identifier. This ID is in the format container_name.group_name.index, where container_name is the name of the OC4J instance, group_name is the name of the OAS defined group to which the container belongs, and index is an integer beginning with 1 and incremented for each JVM started.
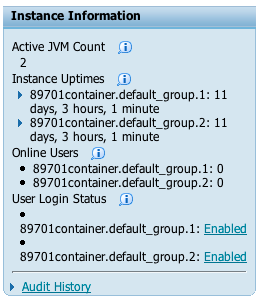
Shown above is the runtime summary displayed within the management page for a JAS server. It shows the number of active JVMs (2) and the uptime, online users, and login status for each JVM. Selecting a runtime metric, in this case JDBJ Database Caches, will display the metrics separately for each active JVM:
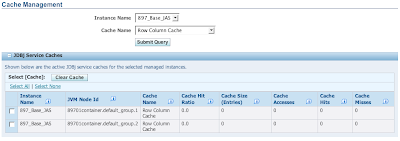 Configuration
ConfigurationEach JVM will utilize the same configuration files. As such it is not necessary to configure items for each JVM. In fact, it is not possible to configure items separately for each JVM.
Log Files
Since each JVM utilizes the same configuration files, including the jdelog.properties file using to configure the E1 logging, creating and writing to the log files would historically conflict in a multi-JVM environment. Tools release 8.97 will now automatically detect a multi-JVM environment and append the JVM ID, described above, into the filename for JVMs with a process index of 2 or greater as shown below:
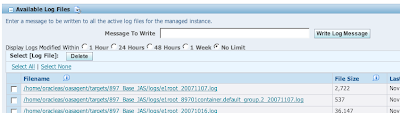
Compatibility
Multiple JVM configuration is supported only for the EnterpriseOne HTML (JAS) server. Configuring multiple JVMs for the other E1 web products, such as the Transaction Server, PIMSync Server, or Business Services Server is not supported and may cause unpredictable results.
UPDATE:
While playing around with this I discovered that making changes to the JVM count on a running container will take effect immediately. That is if you have a container that is configured for a single JVM and change the value to 3 you will see two more java processes appear (after a few minutes). Changing this back to 1 will shut down the additional JVMs. Note: I do not know if it will shut down JVMs with active users on it.
This is pretty cool and can be used to aid a HTML server that is getting overloaded without having to restart it.
Configuring the HTML Server (JAS) Template Configuration
I've often been asked what individual settings must be configured in order for a new HTML server to be functional immediately. First navigate to the 'Server Groups' page
 Next select the 'Configure' icon for the group you wish to modify
Next select the 'Configure' icon for the group you wish to modify Navigate to the 'EnterpriseOne HTML Server' section
Navigate to the 'EnterpriseOne HTML Server' section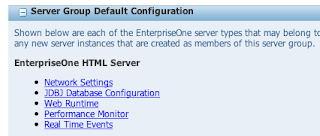
Configure the following settings:
- Network Settings -> JDENET Configuration -> Outgoing JDENET Port - Specify the JDENET port used by the enterprise server
- Network Settings -> Security Server Configuration -> Primary Security Server - Specify the machine name of the enterprise server to use for security services
- JDBJ Database Configuration -> JDBj Bootstrap Datasource - Configure this section to point to the location of the system tables (e.g. System - 812). You can find these values in the JDE.INI of a development client.
- JDBJ Database Configuration -> JDBC Drivers - If you are using the SQL2005 or DB2/UDB on Itanium you may need to change the default JDBC driver
- JDBJ Database Configuration -> JDBj Bootstrap Session -> Bootstrap Environment - Specify a valid environment that will be used to determine the location of various system tables through OCM
- JDBJ Database Configuration -> Oracle Database Settings -> File Contents - If you are using an Oracle database cut and paste the contents of the TNSNAMES.ORA that the server should use.
- JDBJ Database Configuration -> JDBj Spec Datasource - If you define your serialized objects tables (F989998 and F989999) in a particular datasource rather than using OCM to determine their location complete this section
- Web Runtime -> Web Runtime -> Pathcodes - Specify a single pathcode to use for this server. Note it must be surrounded by parenthesis and single quotes, such as ('DV812')
- Web Runtime -> Web Runtime -> Default Environment - Specify the default environment to display in the login form
One last note: when a new server group is created the template configuration is copied from the default server group. Configuring the default server group prior to creating additional server groups means you don't have to reconfigure these items for each new group unless a change to these particular settings is required.
Active Server Manager Users
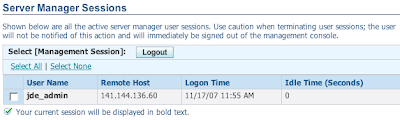
Here's a real quick one: I was asked today if it is possible to know who all is signed in to the management console. To see this simply navigate to the management console instance (Instance Name: home) and select the 'User Sessions' runtime metric on the left. You'll see a grid containing all the active management console users. Your current session will be highlighted in bold.
Troubleshooting Agent Communications
management.server.port=14501
The agent will use this information to attempt to connect to the management console. If unsuccessful, for example if the console isn't running, the agent will continually re-attempt the connection. This activity is recorded in the agent's log files. Look in the log file e1agent_0.log (the zero will always be the most current log) located within the install_location/logs directory of the managed home. In the log file you will see something along the following, in this case the management server is on denlcmwn5.mlab.jdedwards.com and the JMX port is 18501:
If the connection could not be established a corresponding error will appear shortly in the log file.
Tip #1
On the machine the agent was installed attempt to ping the management console using the server name configured in the agent.properties file. If the ping is not successful you may either change the agent.properties file (for example to not use a fully qualified name) or modify host files (e.g. /etc/hosts on unix) as necessary. Either way restart the agent after making any changes.
Tip #2
If the ping was successful you can attempt to telnet to the management console using the same port. For example 'telnet denlcmwn5.mlab.jdedwards.com 18501'. If the connection is successful you know the agent is able to establish a connection to the console. If this fails there may be firewall or other networking issues preventing the connection that need to be resolved. Note: On a successful connection you may ignore any content displayed in the connection; it will not be human readable.
Once that connection has been made the management console will assign a TCP/IP port that the agent should use to listen for incoming connections. The agent will pass in it's machine name and install location, and the console will provide the next unused TCP/IP port starting at the 'Management Agent Starting Port' which was also configured during the installation wizard and defaults to 14502.
In the managed home agents log you will see the port that was assigned, in this case it was 18607:
If everything has been successful so far we will now focus our attention on the logs for the management console. You may view these logs using the console application itself. Navigate to the managed home for the management console (the managed home that contains the 'home' instance). On the bottom of that page select the log file home_0.log. The log should contain an entry indicating the initial connection (thus a port of -1) from the managed agent:
FINER: Received heartbeat from the remote management agent on denlcmlx2 listening on port -1 of type 2 in managed home /home/oracleas/oasagent
Next you will see an entry about the calculated port discussed above.
FINER: Determining the port the remote agent 'denlcmlx2' should start listening on.
Followed by a "heartbeat" request from that agent:
Finally the console will attempt to connect to the remote agent on the port assigned. If successful you will see something like:
Tip #3
If there are errors indicating the connection was not successful follow similar steps as above to troubleshoot the issue:
- On the management console machine ping the server using the name reported in the log files (in this case denlcmlx2). If not successful ensure the network/dns configuration is correct. Add an entry to the hosts file (\windows\system32\drivers\etc\hosts) for the machine name if necessary.
- If the ping was successful telnet from the management console to the specified name and port, for example 'telnet denlcmlx2 18607'. If that connection was not successful ensure that there are no firewall or other networking issues preventing the connection.
Tip #4
On the iSeries platforms if there are errors in the logs indicating crypto or encryption related problems (because the connection between agents is fully encrypted) this usually indicates the required JDK (1.5) is not present.
Understanding the Server Manager Downloads
If you are installing SM for the first time I would recommend obtaining the latest installer. This will be a large (1 GB) download that is used to perform the initial installation.
If you have already installed SM you may download a significantly smaller update (around 30-50 MB) and apply that to your existing SM installation (of course using SM to perform the update).
For example installing 8.97.0.0 and then applying the 8.97.0.1 update will be functionally identical to initially installing the 8.97.0.1 release. You may also go backwards, if desired, to an earlier release.
Remember you may always use the latest SM release even if you are managing earlier tools releases of the E1 components. Using the latest SM release ensures you have all the latest bug fixes and functionality available.