iMERGE Group
How can I remove a URL on my website from the Google Index?
To remove a specific URL (for example, the page http://www.example.com/page4.html) of your own website from Google’s index, there are two options available:
Table of Contents
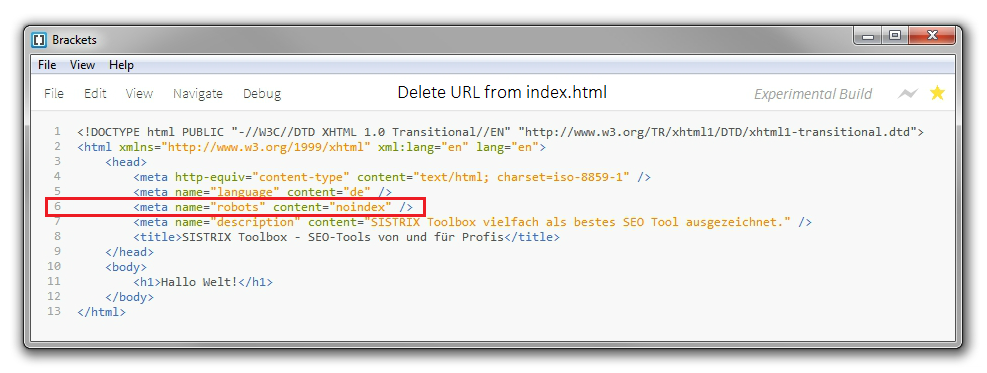
Add the meta-element robots to the source code of the page which is not supposed to appear in the index and set the value to NOINDEX.
By adding the following to the source code of a page, it will be removed from the index:
<meta name="robots" content="noindex">You have to add the meta-element in the <head> area of the specific page:
If the page already has the robots meta-element with the value INDEX, you can simply replace it with NOINDEX.
Done. Now you just have to wait until the desired URL is removed from the Google index.
By using the meta-robots value NOINDEX, the URL will also be removed from the index of Microsoft’s search engine Bing.
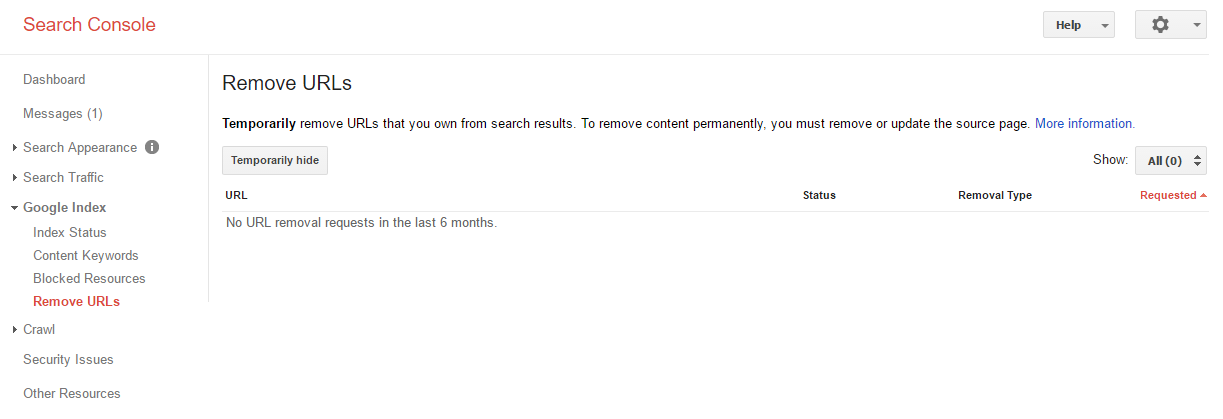
Option #2: Use the Google Search ConsoleUsing a setting within the Google Search Console, you are able to easily have a URL removed from the Google index.
In case you are not yet using the Google Search Console, you can activate your website for the free (www.google.com/webmasters/tools/?hl=en) in just a few minutes. This also lets you remove URLs from the Google Index afterwards.
Removing a URL from the index with the Google Search Console:
- Log into the Google Search Console and select the desired website
- Click on “Optimization” in the left-hand navigation
- Click on “Remove URL” in the sub-menu
- Click on the button “create a new request for removal” on this page
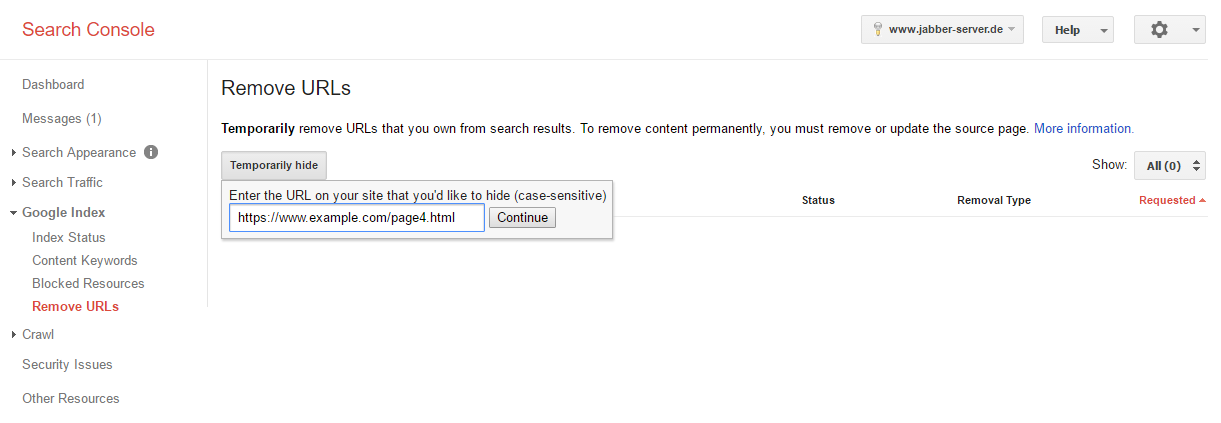
- You will now be asked to type in the URL of the page that you want to be removed and confirm your choice by clicking on “continue” (in our example this is the page http://www.example.com/page4.html)
Done. Now you have to wait some time until the desired URL is removed from Google’s index.
The Google Search Console will now also indicate the status of the removal process of the URL on this page.
The search engine Bing also provides their own webmaster tools, which you can use to have URLs removed from their index.
Tip(http://www.bing.com/toolbox/webmaster)
If you use option #2 to remove a URL from the index, by using the Google Search Console / Bing Webmaster-Tools, the deletion may only be temporary in some cases.
The URL will definitely be removed from the search index for 90 days. Afterwards, there is a possibility that the URL may be re-introduced into the index, if the URL is still accessible and links still point to it.
If you want to make sure that a URL is permanently removed from the index, you should go with option #1 and use the robots meta-element with NOINDEX.
Categories: DBA Blogs
How to Remove Japanese SEO Spam from your Website ?
Discovering the Hack1. Identify infected pages using Google Search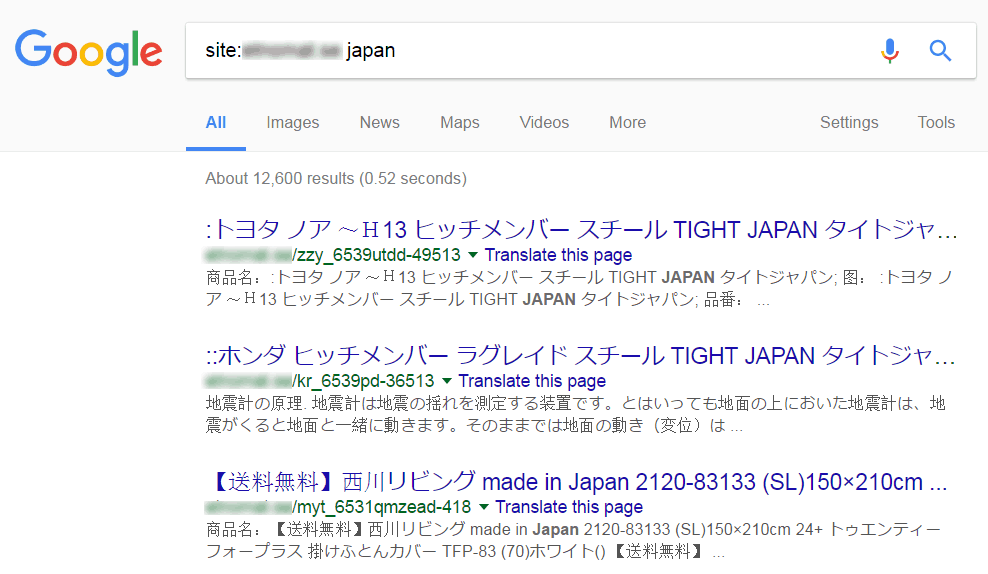
2. Verify with Security Issues Tool in Google Search Console 3. Fetch as Google to check for ‘Cloaking’
3. Fetch as Google to check for ‘Cloaking’
You can uncover such pages by opening Google Search and searching for:
site:[your site root URL] japanNavigate through some pages of the search results to see if you discover any suspicious looking URLs. These are the pages indexed by Google containing the word ‘japan’. If you notice pages with the Japanese characters in the title or description, it is likely that your website is infected.

In your Google Search Console (earlier called Google Webmaster Tools), navigate to the Security Issues Tool in the left sidebar.

When you visit any of these hacked pages, you might see a 404 not found page suggesting that the web page doesn’t exist. Be careful, the hacker may be using a technique called cloaking. Check for clocking by using the “Fetch as Google” tool in your Google Search Console.
Fixing the Japanese SEO Spam Hack1. Remove any newly created user accounts in the Search ConsoleIf you don’t recognize any users in the “Users and Property Owners” tab, immediately their revoke access. Websites hacked with the Japanese SEO Spam add spammy Gmail accounts as admins so that they can change your site’s settings like sitemaps and geotargeting.
2. Run a Malware ScanScan your web server for malware and malicious files using the ‘Virus Scanner’ tool in the cPanel provided by your web host.
3. Check your .htaccess fileHackers often use the .htaccess file to redirect users and search engines to different malicious pages. Verify the contents of the .htaccess file from a last known clean version of the file from your backups. If you find any suspicious code, comment it out by putting the ‘#’ character in front of the rule.
4. Check Recently Modified FilesLogin to your web server via SSH and execute the following command to find the most recently modified files:
find /path-of-www -type f -printf '%TY-%Tm-%Td %TT %p\n' | sort -rIf you are an Astra customer, you would have received an email telling you about malicious file changes.
5. Check your SitemapA hacker may modified, or added a new sitemap to get the Japanese SEO Spam pages indexed quickly. If you notice any suspicious links in the sitemap, ensure that you quickly update your CMS core files from a last known clean backup.
6. Prevent future attacks with a Website FirewallAnother option to prevent the Japanese SEO Spam infections is to use a Website Firwall.
If you are still looking for an expert then feel free to reach out to us at support@ingressit.com and someone from our team will surely help you.
Categories: DBA Blogs
Oracle 12c New Feature - Temporary Undo
As we all know Oracle database always contains a set of system related tablespaces such as SYSTEM, SYSAUX, UNDO & TEMP, and each of them are used for different purposes within the Oracle database. Pre Oracle 12c R1, undo records generated by the temporary tables used to be stored in undo tablespace, much similar to a general/persistent table undo records. However, with the new feature introduced in 12c R1 temporary undo, the temporary undo records can now be stored in a temporary table instead of stored in undo tablespace.
Benefit of temporary undo Reduction in undo tablespace and less redo data generation as all this information won’t be logged in redo logs. Also this feature is flexible and DBA can enable the temporary undo option either at session level or database level.
Enabling temporary undoTo enable this new feature, the following needs to be set:
Compatibility parameter must be set to 12.0.0 or higher
Initialization parameter TEMP_UNDO_ENABLED needs to be enabled
As described above all the temporary undo records are now stored in a temp tablespace, we need to create the temporary tablespace with sufficient space
For session level, we can use: ALTER SESSION SET TEMP_UNDO_ENABLE=TRUE;
Important V$ ViewsThe dictionary views listed below are used to view/query the information/statistics about the temporary undo data:
V$TEMPUNDOSTAT
DBA_HIST_UNDOSTAT
V$UNDOSTAT
If we would like to disable this feature, we need to execute the below statement:
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM|SESSION SET TEMP_UNDO_ENABLED=FALSE;
Benefit of temporary undo Reduction in undo tablespace and less redo data generation as all this information won’t be logged in redo logs. Also this feature is flexible and DBA can enable the temporary undo option either at session level or database level.
Enabling temporary undoTo enable this new feature, the following needs to be set:
Compatibility parameter must be set to 12.0.0 or higher
Initialization parameter TEMP_UNDO_ENABLED needs to be enabled
As described above all the temporary undo records are now stored in a temp tablespace, we need to create the temporary tablespace with sufficient space
For session level, we can use: ALTER SESSION SET TEMP_UNDO_ENABLE=TRUE;
Important V$ ViewsThe dictionary views listed below are used to view/query the information/statistics about the temporary undo data:
V$TEMPUNDOSTAT
DBA_HIST_UNDOSTAT
V$UNDOSTAT
If we would like to disable this feature, we need to execute the below statement:
SQL> ALTER SYSTEM|SESSION SET TEMP_UNDO_ENABLED=FALSE;
Categories: DBA Blogs